CPU speed
Traditionally clock speed is what is used to measure the speed of a CPU. However this is no longer an accurate way of comparing CPU’s. However it still has some relevance, especially if you are considering over clock a CPU. (Forcing it to run faster than normal).
A clock cycle is the amount of time it takes the CPU to resynchronize itself. This means it must be at least as long as the time it takes the longest signal to propagate through the CPU. Putting it more simply it is the amount of time a single instruction takes to run. As such in ten clock cycles you should be able to run ten instructions. This is a over simplification however it will serve our purposes.
Processor speeds tend to be shown as a frequency. Lets take a average value of 2 Ghz as a example. We can calculate the amount of time it takes to run one cycle. As you can see from the calculation below it is a tiny value.
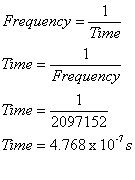
2 Ghz = 2048 Mhz = 2097152 Hz
Effectively the frequency says how many instructions it can run in a second, or more specifically how many clock cycles it can do per second. This, however, is not enough to use as a benchmark. Processors are getting to the point where it is hard to increase the clock speed. As such CPU manufacturers such as AMD or Intel are trying other methods. In order to fairly compare these CPU’s you need to compare them running controlled tests. An excellent place to see benchmarks of different CPU’s is www.tomshardware.com.

